Acoustic barriers are essential elements in the mitigation of ambient noise, protecting both the public’s well-being and commodity. In this article, we are set to explore each detail of these acoustic barriers, the available types, their advantages and, finally, their utility in different contexts. Read on!
Example of an acoustic barrier: Stratocell Whisper absorbent panel
What are acoustic barriers?
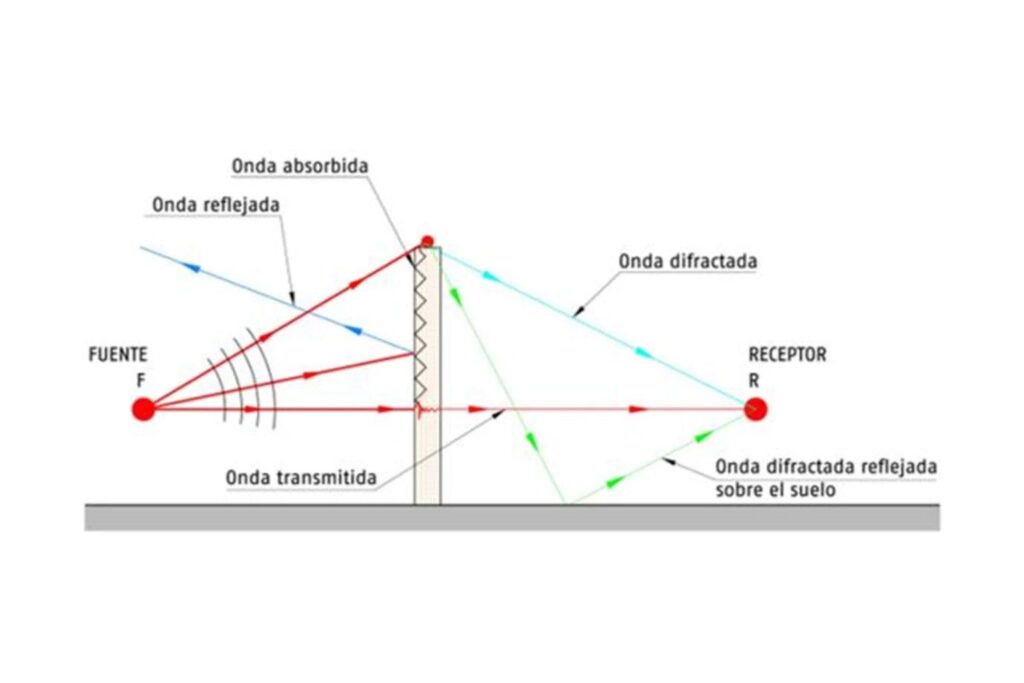
Acoustic barriers or screens are those elements or devices which, when placed between the source and the receptor of a sound and rightly measured, they become a screen that interrupts the spread path of sound waves to create what is known as an “acoustic shadowing” next to the receptor by “diffraction” of the sound waves in its edges.
That is a phenomenon which affects the spread of sound, making the acoustic energy dissipate at the edges of the objects that are non-permeable to sound (acoustic screens) that it finds during its path. It is explained by the Fresnel-Huygens principle and the magnitude of the effect depends on the relation between the wavelength and size of the obstacle.
Types of acoustic barriers
There are different types of acoustic barriers, each one with traits and applications of its own:
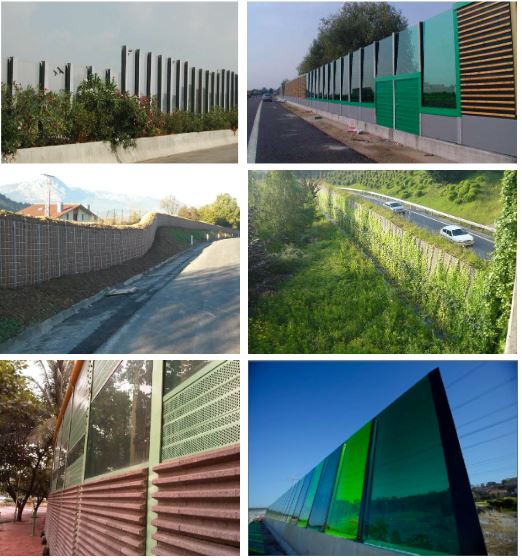
Reflective or diffractive barriers
They have the same goal, which is to protect noise-sensitive areas from the traffico of roads, highways or railroads, canalizing the sound to either one or both sides depending on the distance and height of the space that needs protection. They can be opaque, translucent and transparent. Such barriers are placed in straight or tilted positions, depending on the size and length of the protected zones.

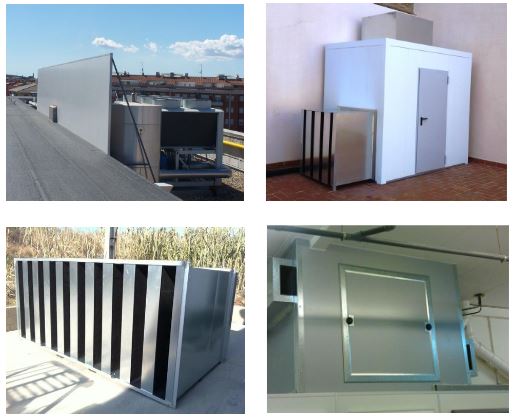
Absorbing acoustic barriers
Commonly used in industrial zones to reduce the noise level both inside and outside facilities, engines, air ventilation structures, etc. They generally use a combination of absorption and perforated plate. Commonly found near or on engines, A/C central units or industrial structures. They can be present both indoors or outdoors, either fixed or mobile.

Common materials
- Metal: Offers durability and flexibility in the reflection of sound.
- Transparent (plastic or glass): Give full visibility while still blocking the noise.
- Concrete: Very effective in the absorption and diffraction of sound.
- Wood: Used for aesthetic and environmental applications
- Plant material::. Combines environmentally friendly solutions with landscaping.
- Combinations:. Two or more of these materials are often used together to optimize their acoustic and aesthetic responses.

Advantadges of acoustic barriers
- They accomplish the reduction of environmental noise produced by traffic, transportation or industries that affect our homes, workplaces, schools, hospitals or any other kind of building.
- They keep workers or pedestrians away from spots in which the noise produced by the machinery or any other source exceeds the maximum intensity of sound allowed in any potential local regulation for environmental or health protection.
- Reducing acoustic contamination
Main uses for the acoustic barriers
To deflect or absorb any excessively loud noise in the same spot where it comes from, meaning that we can carry on with our everyday activities without having our health directly or indirectly suffer from it.
In case of any doubt, do not hesitate to contact us