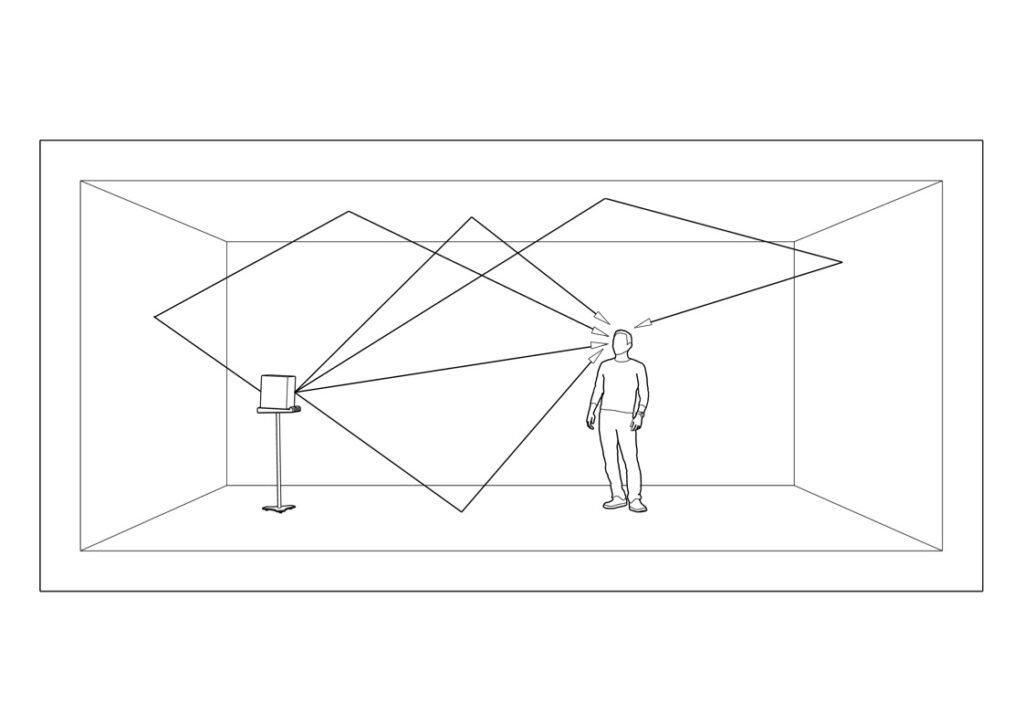
Reverberation: Meaning
Reverberation is defined as the persistence of sound after its source has stopped making it. This phenomenon is caused by the reflection of sound on the different surfaces of a room, including walls, ceilings, floors, and furniture. these reflected sound waves make the sound energy persist, creating a reverberant sound. even the number of people present in a room affects reverberation. in an empty space, reverberation will last longer compared to a space full of people.
Reverberation time: How is it measured?
Reverberation time is measured in seconds and is determined by the use of a sonometer (also known as sound level meter). This device measures the time gone by from the moment when the original sound source is halted until the intensity of the sound has decreased by 60 decibels (or 60 dBs). This method, known as RT60, was developed by Wallace Clement Sabine. For more specific and less invasive measurements, other methods such as RT30, RT20, RT15 or RT10 can be used, as they do not require reaching such loud levels of sound.
Here at Mas Acoustics we provide reverberation time measurement service TR60 according to ISO 3382 ruling.
Difference between echo and reverberation
The main difference between echo and reverberation lies in the distance and perception of the reflected sound:
- Echo: A reflected sound which is heard from over 17 meters away from its source location. It travels for 50 ms from its source to the listener and takes another 50 ms to return to its original point. At that point, it is perceived as a different sound from the original one.
- Reverberation: It occurs when sound reflections arrive from less than 17 meters away, being perceived as the same sound as the one coming from its source location.
Although both phenomena can happen in open and narrow spaces, echo is commonly associated with wide, open places and reverberation goes along with closed rooms.
Types of reverberation and their effects
There are two kinds:
- Acoustic reverberation in a room: It is produced by the reflection of sound in a room or exterior space. This type of reverberation must be regulated in conference rooms, classrooms, recording studios and concert halls, adjusting the reverberation time according to the needs of each space.
- Artificial or emulated reverberation: Used in recording studios and multimedia production. Known as “reverb”, this technique modifies the sound of instruments and voices recorded in said studios with no reverberation with the use of electronic devices or emulation software to obtain a more organic sound. An example of artificial reverb would be the sympathizers that include a spring and its own regulator. For digital emulations, see the Lexicon 224 Digital Reverb Plug-in.
Here you can also see the UA Ocean Way Studios Plug-in, with which you can adjust an instrument track in the same fashion as changing the color of the recording track with different microphones, including the position of the instrument within that mythical recording studio:
What is the purpose of reverberation and why is it important?
Acoustic reverberation within an enclosed space can be used in favor of our purposes if we use it to allow people in an auditorium to listen to live music from an orchestra without need for any amplification. To achieve that, the most common procedure is to combine acoustic absorption in the surfaces in which we do not want any reflections and acoustic diffusers with adequate tilt angle so that each sector of the audience in the hall can listen to the music as it is being played in that instant, as a lone direct sound with no reflection.
Greek or Roman amphitheaters had remarkable acoustics thanks to an oval architectural design, in which marble diffusers were used in a way that allowed the sound waves to bounce efficiently across surfaces, ensuring the entire audience be able to hear all the details of theatrical representations from a distance even greater than 100 meters away in the case of the Roman Colosseum.
When we talk about reverb or reverberation while editing an audiovisual production, it becomes useful in order to achieve an organic sound or to highlight certain frequencies, drums, any other instrument or the narrative voice itself.
FAQ about reverberation
How to remove reverberation from a recording?
To remove undesired reverberation from a voice or instrument recording, audio plug-ins are able to filter excess reverb. An example of such plug-ins is UAD CAMBRIDGE EQ, which allows the user to adjust and highlight specific sequences.
How to remove reverberation from a room?
Using absorption materials in the right proportion—without overdoing it—will reduce reverberation across different frequencies, resulting in a more balanced sound. For spaces used to play or record instruments, we recommend covering 20–40% of the walls and ceiling with 5 cm thick acoustic panels and adding some bass traps.
The Auralex Project 2 Roominator kit covers the minimum recommended 20% of absorption material in rooms of 7 to 12 m². Check out this post: How to turn your room into a studio, to see how to properly distribute each component.
The ideal reverberation time depends on the size of the room, as well as its intended use. For example, in a 200 m³ room designed for conferences, the recommended RT is 0.7 seconds. However, if the audience will be listening in a language that is not their native one, it is advisable to reduce the RT to around 0.45 seconds for better intelligibility.
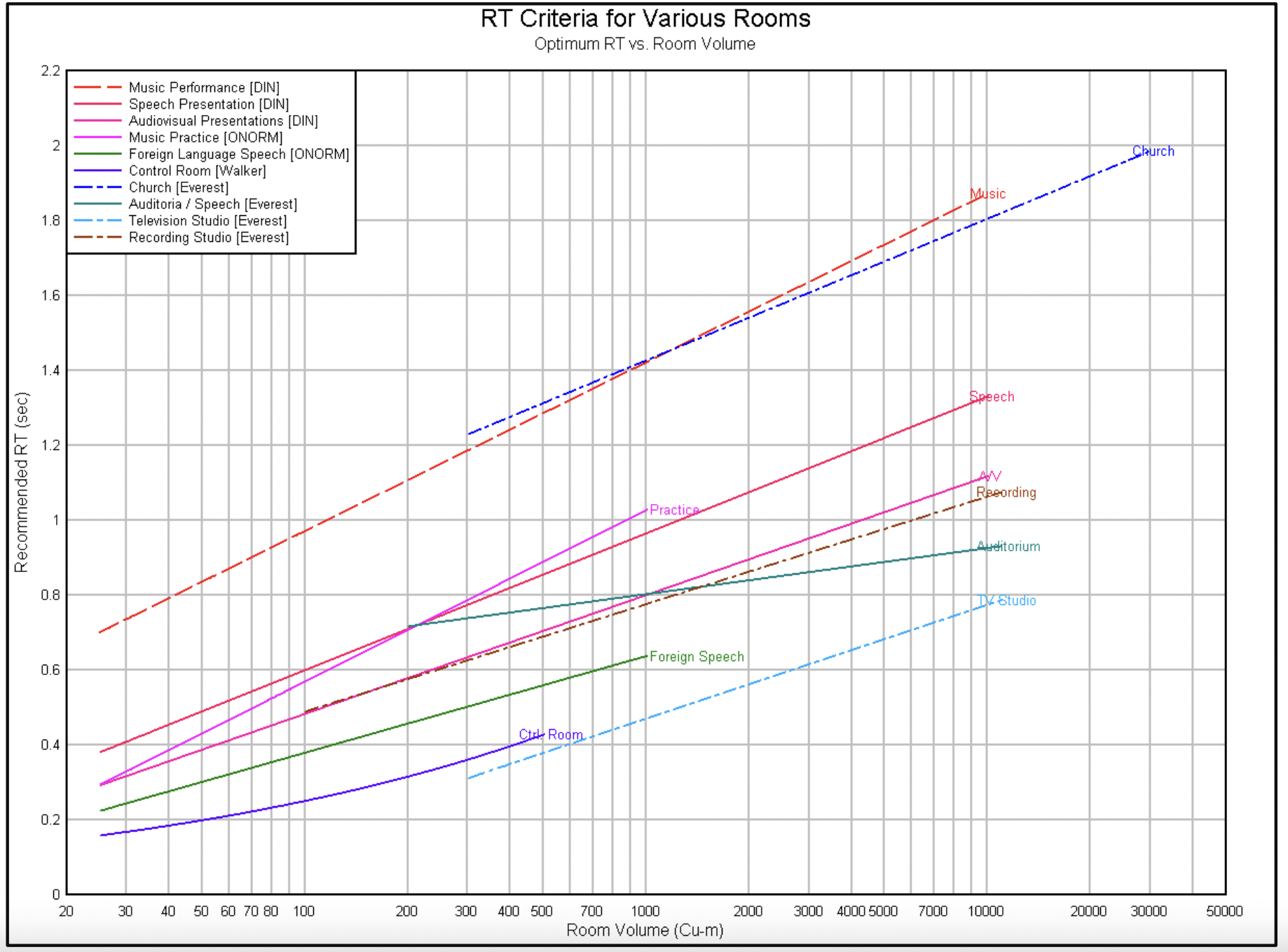
Jonathan Sheaffer-Prediction and Evaluation of RT Design Criteria-Sep-2007″ (https://www.arauacustica.com/files/publicaciones_relacionados/pdf_esp_23.pdf)
How does reverberation impact music and speech?
Excessive reverberation can harm the quality of sound inside of an enclosed space:
- Music: High reverberation can make certain musical details get lost or distorted, lowering the clarity and precision of sound.
- Speech: In environments such as a classroom or a concert hall, excessive reverberation diminishes the intelligibility of speech, which can result in up to 50% loss of the speaker’s message.
In this TED video, Julian Treasure illustrates how reverberation time reduction can significantly improve intelligibility and speech, proving the importance of good acoustic care in these environments.
Understanding and controlling reverberation is essential to optimize the quality of sound in different spaces, improving both the auditory perception and the general experience in many endeavors.
If you have any doubt please feel free to contact us.